Riparian Areas and Wetlands
Many of CCBWQA projects re-integrate the stream channel and floodplain along the corridor of Cherry Creek and its tributaries. Re-integration will cause more frequent stormflows to spill out of the channel onto the riparian and floodplain area, and increase filtration/infiltration in the overflow banks. Revegetation along the corridor with wetland plants, grasses, shrubs, and trees provides an aesthetic buffer and promotes enhanced riparian habitat.
Riparian preservation is protection of natural or present condition of a riparian area to prevent its destruction, degradation, or alteration in any manner.
Protection Models
CCBWQA began exploring riparian protection programs that have been implemented in other areas in Colorado, such as:
- Land acquisition
- Conservation easements
- Riparian Buffers and Setbacks
- Overlay Zoning
- Cluster Development
- Dendritic Development
Next steps will be dependent on both the findings of the watershed model, and interest from potential partners.
Why Stream Preservation?
A stream corridor encompasses an active channel and floodplain surfaces above and outside of the channel banks. Riparian areas are adjacent to streams, rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands. Riparian areas act as buffers between upland areas and the stream, and help filter pollutants like nutrients and sediment. Properly functioning stream and riparian areas are critical to maintain water quality, water flow, riparian habitat, wildlife, fish populations, and diversity, as well as protect downstream beneficial uses.

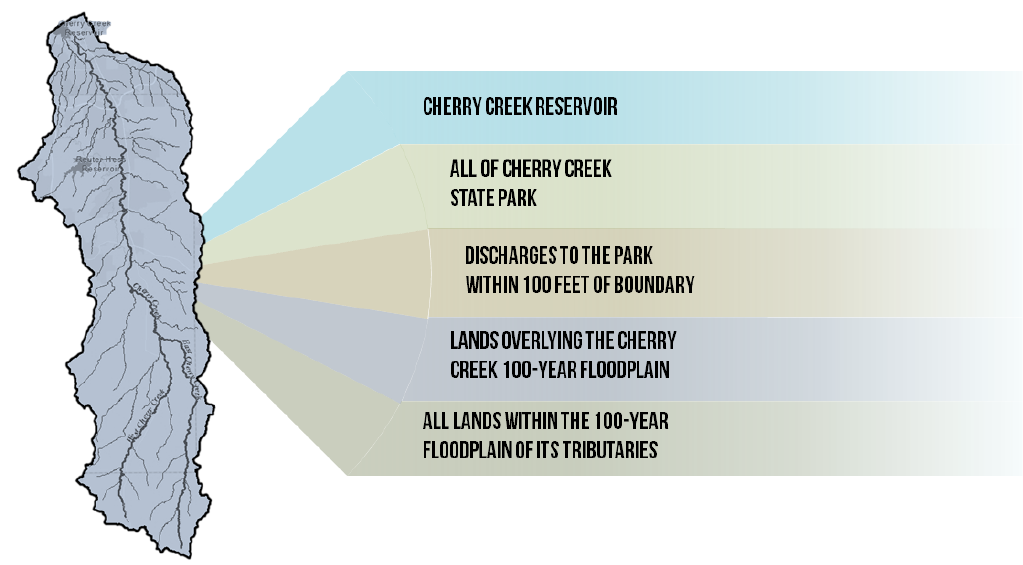
Stream Preservation Areas Defined in Regulation 72
Benefits to a Healthy Riparian Vegetation Area
A healthy riparian vegetation area:
- check_box Reduces stream bank erosion, which maintains stable stream channel geomorphology and reduces velocity of flow;
- check_box Provides support of sediment deposition on floodplains during periods of overbank flow, which removes total suspended sediments and attached phosphorus that can degrade water quality;
- check_box Provides shade, which works to lower water temperatures (lower water temperatures support higher dissolved oxygen levels which are important to maintain fisheries); and
- check_box Removes phosphorus, nitrogen, and sediment from surface runoff (through plant uptake and filtering and biogeochemical interactions between surface and ground water).
