2022 Report
Special Studies
Highlights:
In 2022, CCBWQA completed and embarked on several special studies to better understand conditions in the watershed and opportunities to reduce pollutant loading to the Reservoir.
These studies included:
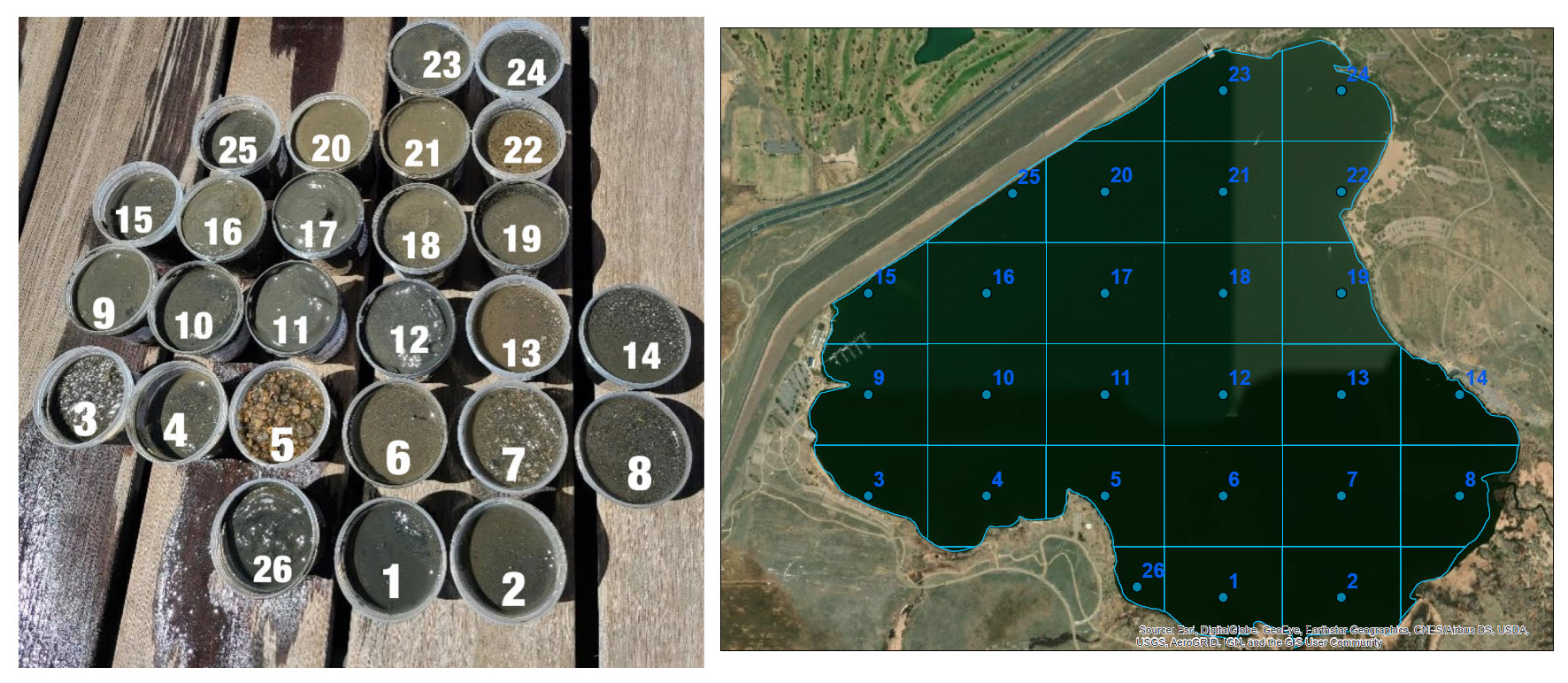
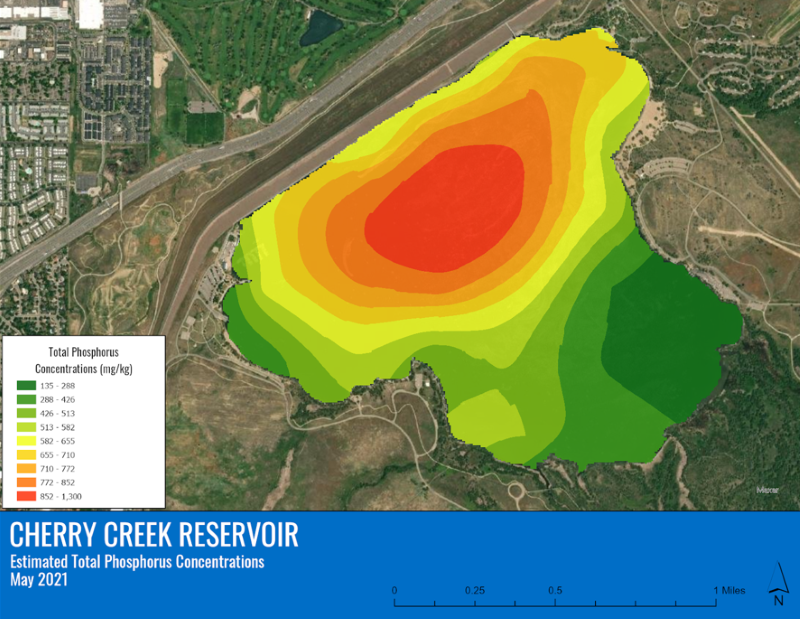
- Sediment Nutrient Concentrations: In 2022, a study was completed on the sediment nutrient concentrations in the Reservoir. The nutrient storage and internal loading potential information is useful for future management considerations.
- Wetlands Harvesting Pilot Project: In 2022, CCBWQA completed year two of a six-year project to cut and dispose of wetland vegetation to reduce phosphorus and nitrogen from being carried to Cherry Creek Reservoir after the plants decay.
- Cherry Creek Stream and Water Quality Assessment Study: CCBWQA worked with Muller to conduct a comprehensive stream assessment of Cherry Creek from Cherry Creek Reservoir upstream to the State Park boundary to identify risks to Reservoir water quality and Park resources and infrastructure. The study recommended rehabilitation of Cherry Creek and Piney Creek through the Park and in degrading reaches upstream.
- BMP Effectiveness Study: In 2022, Regulation 72 stormwater requirements were “modernized” to be consistent with the current state of the practice for reducing pollutant loads from stormwater. As a companion effort, CCBWQA began a study to synthesize the most current information on the expected effectiveness of stormwater BMPs (also known as stormwater control measures). This study will be completed in 2023.
- Receiving Pervious Area Study: CCBWQA is partnering with SEMSWA and the Mile High Flood District to develop a more quantitative understanding of volume reduction benefits of receiving pervious areas such as grass buffers, grass swales and other landscape areas. By reducing runoff volumes through use of receiving pervious areas, pollutant loads can be reduced, as well as channel erosion. Use of receiving pervious areas is a key principle of low-impact development and green infrastructure approaches to development.
Useful Links

Sediment Sample Study
The wide range of colors and consistencies illustrates the spatial variability of sediment composition throughout the Reservoir. The highest accumulation of organic material was found in the deepest areas (the center) of the Reservoir. The study determined that an average of 10% of the phosphorus in the sediment is mobile or likely to impact water quality through internal loading which could drive algal blooms.